3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a manufacturing process through which three dimensional solid objects are created. It enables the creation of physical 3D models of objects using a series of additive or layered development framework, where layers are laid down in succession to create a complete 3D object.
● 16+ years rich experience in SLA, SLS, Metal 3D Printing and ColorJet Printing
● Low Cost, High Quality with Fastest Turnaround in 1 day
● 24/7 Service, immediate responsiveness, instant quote in seconds
● 100% Customer Satisfaction, exceeding your expectation
● Full Series Of The World’s Most Advanced Integrated 3D Printing Equipments
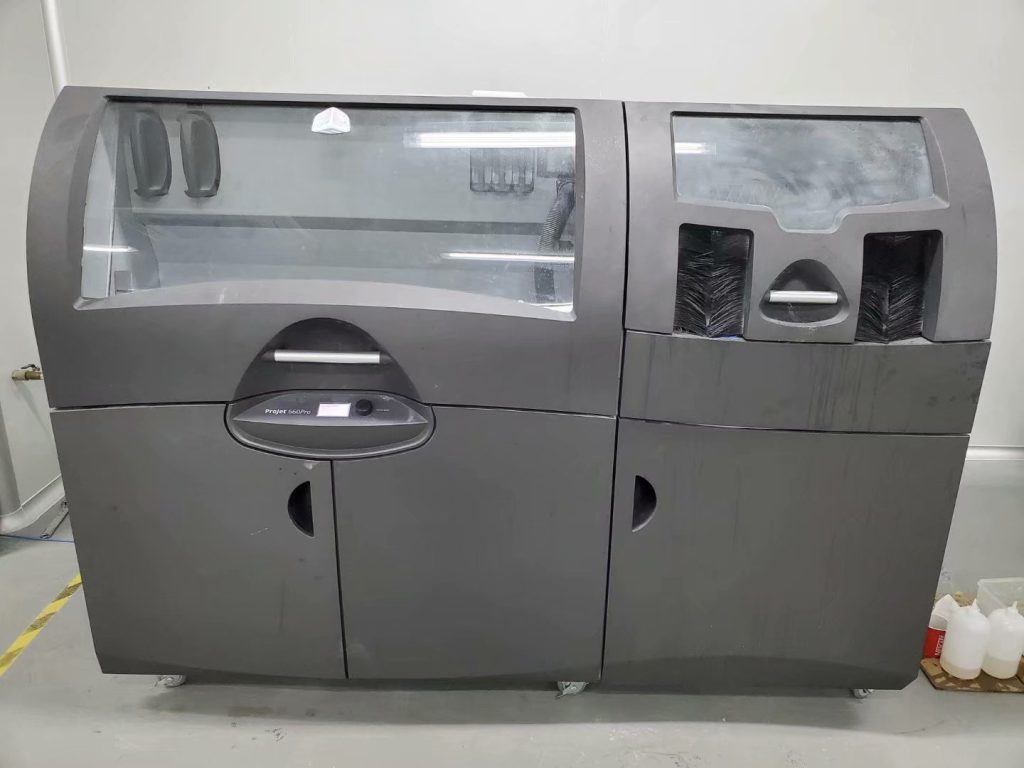



Stereolithography (SLA) Printing
SLA is a popular way to create realistic prototypes and customized products, It’s best used for products where appearance is more important than structural integrity. SLA printing can create intricate structures and complex geometric shapes without increasing the price per unit.
Resins are available in different colors, and clear resin can also be used. However, the products made with SLA printing are not nearly as strong as those made with FDM or another printing method. Durable, heat-resistant, and rubber-like resin materials are available.
SLA printing is typically used to create visual prototypes. SLA parts have a smooth surface finish and often look identical to the final product. SLA printing is also used to make custom end-use products in different colors or with slight visual differences.
SLA is commonly used to create parts and light-duty functional prototypes in the automotive industry, medical instruments, electronics, oil and gas, and for consumer products.
-Master patterns for vacuum casting
-Sacrificial patterns for metal casting
-Tools, molds and dies
-Functional prototypes and models
-High clarity, transparent products and components
-Complex assemblies
-Wind tunnel models
-Under the hood components
-Rapid production of flow test rigs
-Mass customization
-Custom assembly jigs and fixtures
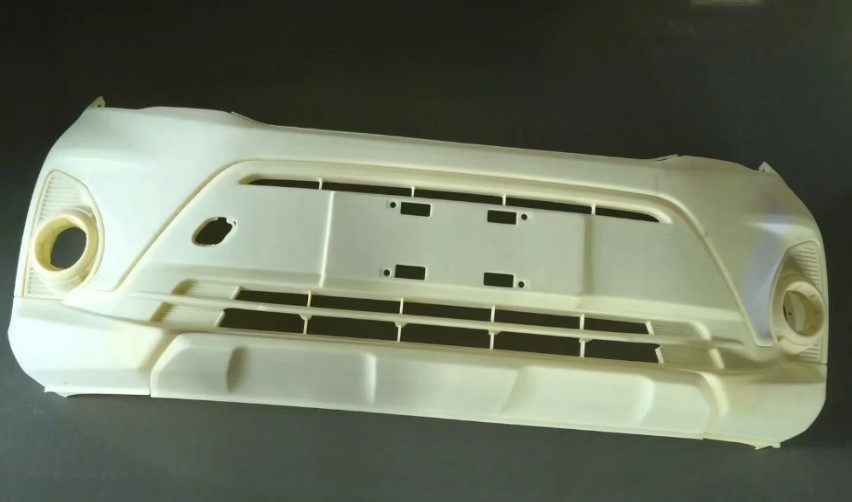
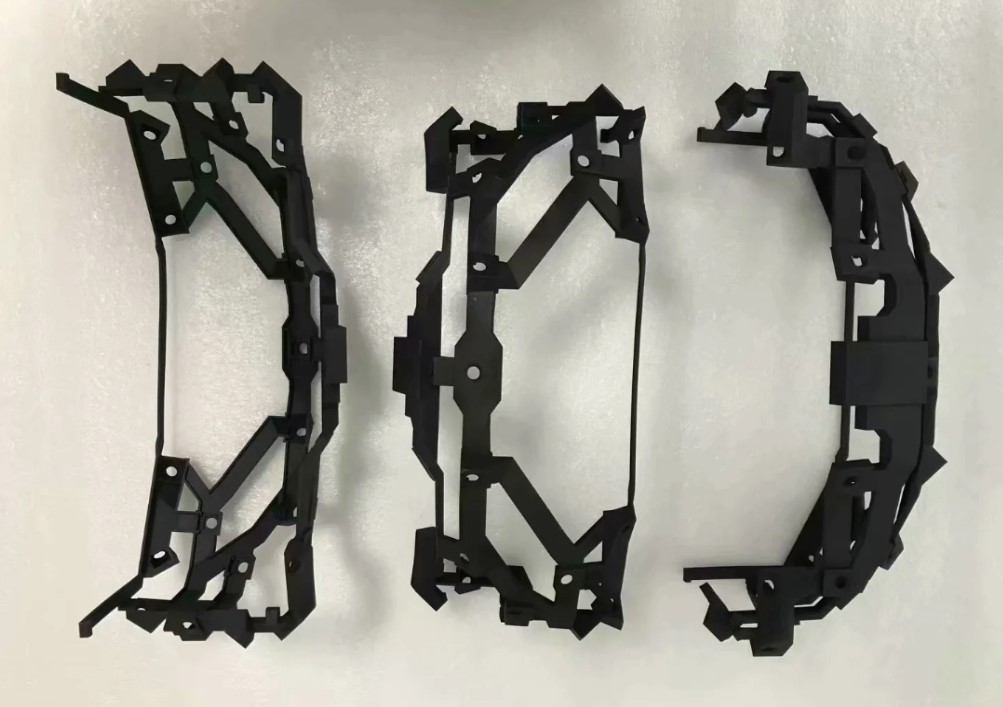


Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a powder bed additive manufacturing process used to make parts from thermoplastic polymer powders. Parts produced with SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
SLS Applications
SLS is commonly used for durable, functional parts for low to mid-volume production, enclosures, snap-fit parts, auto components and thin-walled ducting.
-Complex plastic prototypes and end-use parts
-Complex tooling, parts, and prototypes
-Complex investment casting patterns
-Flexible, functional parts with rubber-like performance characteristics
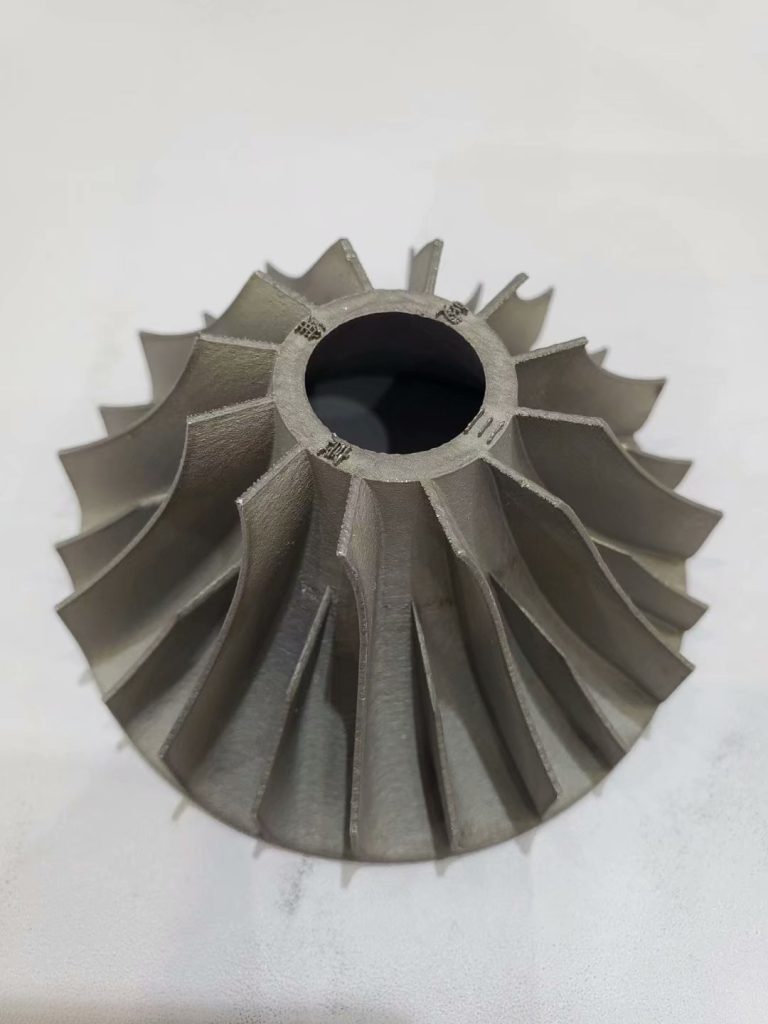
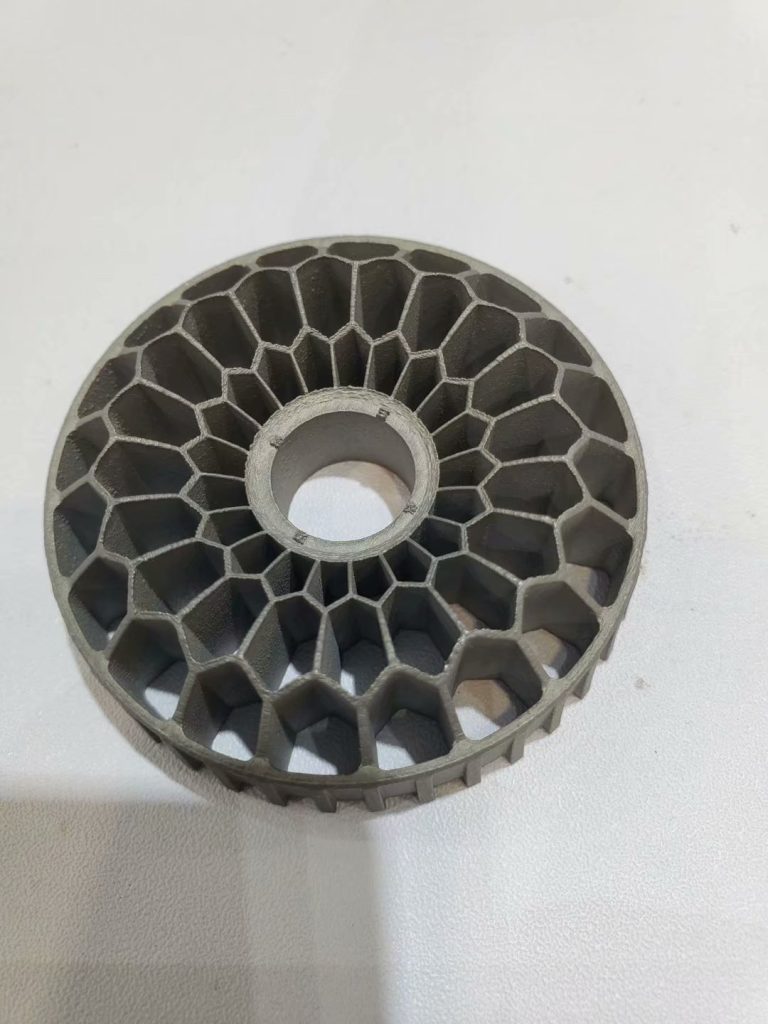
Metal 3D Printing (DMLS)
Metal 3D printing is a revolutionary technology that produces “impossible-to-make” end use metal parts directly from your CAD data. The mechanical
properties of DMLS parts are comparable to cast parts or machined component. We offer 3D metal printing in titanium, stainless steel, maraging steel and
aluminum. Each material has unique advantages relating to mechanical performance, weight, corrosion resistance and more.
The advantage of the process is that the more complex or rich the component is, the more economical the process becomes. 3D metal printed parts are
fully dense, incorporating complex geometries and precise internal features that cannot be made with traditional machining alone.
DMLS Applications
DMLS produces high performance, end-use metal 3D printed parts for industrial applications in aerospace, automotive, medical and others.
-Automotive components – lightweight performance and racing parts
-Medical – orthopaedic implants, medical devices, surgical tools
-Tooling – inserts with conformal cooling and heating
-Energy – turbines, complex heat exchangers and heat sinks
-High temperature component applications
-Functional Parts – low to medium volume, high quality parts on demand with direct digital manufacturing
-Prototypes of any complexity
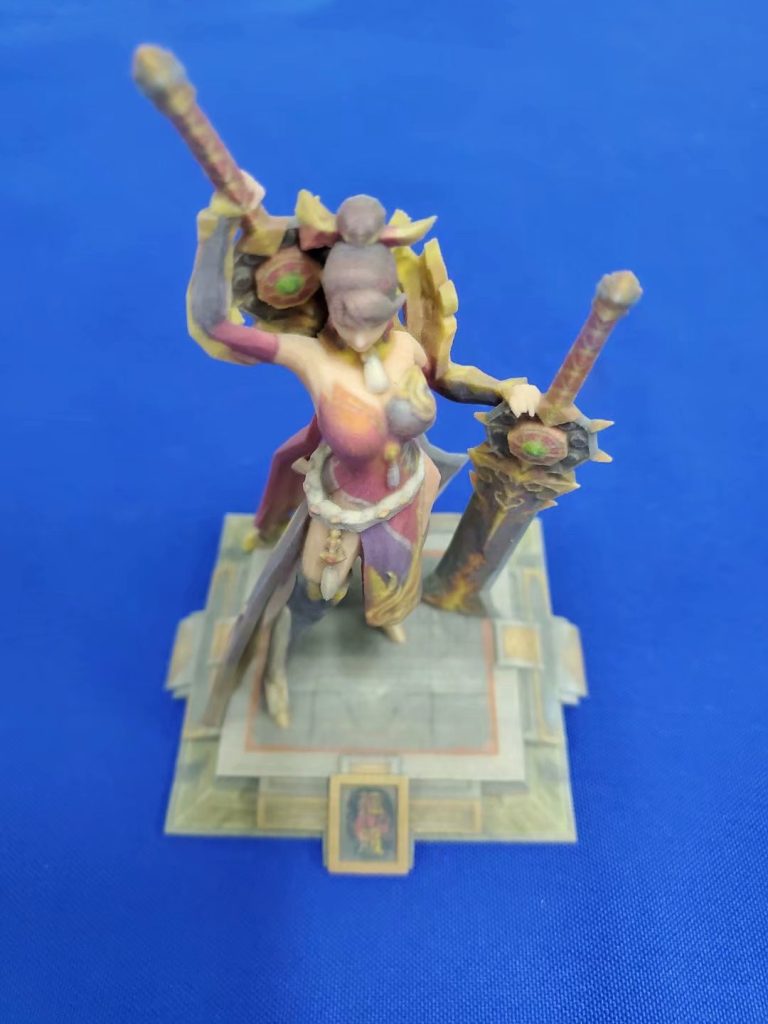
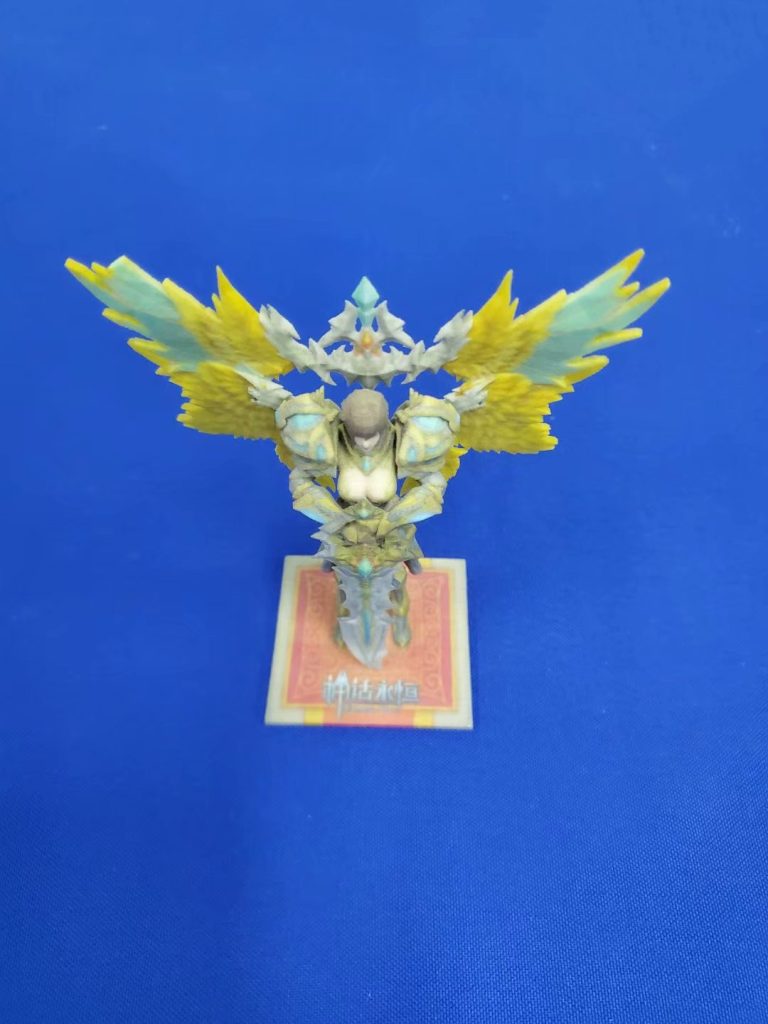




ColorJet Printing (CJP)
ColorJet Printing (CJP) is an additive manufacturing technology which involves two major components – core and binder. The core material is spread in thin layers over the build platform with a roller. After each layer is spread, color binder is selectively jetted from inkjet print heads over the core layer, which causes the core to solidify.
The build platform lowers with every subsequent layer, which is then spread and printed, resulting in a full-color 3D model. Whether printed with color or in standard white, parts can be additionally clear coated to add a hard, smooth coating or wax coated to smooth out the surface finish.
CJP Applications
-Architecture models
-Consumer product design review
-Healthcare surgery verification
-Educational classroom models
-Medical teaching models
-Structural analyses results
-Cost effective, visual display
3D Printing Materials
Plastic Metal
● ABS ● Stainless Steel
● Polylactic acid (PLA) ● Aluminium
● Polycarbonate (PC) ● Copper
● PETG ● Titanium
● PA/PA+GF
3D Printing Finishes
● Sanding
● Polishing
● Bead Blasting
● Clear Coating
● Painting
● Electroplating
● Texturing
● Customized
